Former U.S. National Security Advisor John Bolton asserts that Iran is “in trouble” and its regime is weakening following recent U.S. military actions in Syria and Iraq, targeting Iranian-backed militias. Bolton, a long-time advocate for a hard-line stance against Tehran, made these remarks in an interview, suggesting that the strikes demonstrate U.S. resolve and potentially destabilize the Iranian government.
Bolton, in an interview, stated, “I think the regime is in trouble,” referring to the Iranian leadership. He characterized the U.S. strikes as sending a strong message to Tehran, suggesting that they could have a significant impact on the regime’s stability and influence in the region. “These strikes are a demonstration that the U.S. is willing to respond to attacks on its personnel and facilities, and that can have a real impact,” Bolton explained. He believes that the strikes against Iranian-backed militias serve as a deterrent and could embolden opposition groups within Iran.
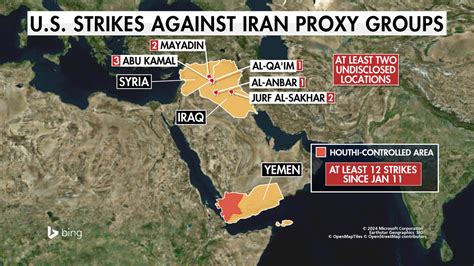
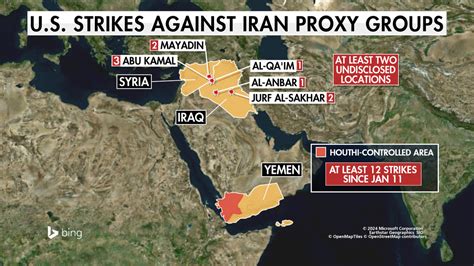
The U.S. military actions, which prompted Bolton’s comments, were in response to a series of attacks on U.S. forces stationed in Iraq and Syria. These attacks, often carried out by groups allegedly supported and funded by Iran, have resulted in casualties and heightened tensions in the region. The Biden administration has stated that the strikes were intended to degrade the capabilities of these militias and deter further aggression.
Bolton’s perspective provides insight into the broader debate surrounding U.S. policy toward Iran. He has consistently argued for a more assertive approach, advocating for measures aimed at weakening the Iranian regime and preventing its pursuit of nuclear weapons. His views contrast with those who favor diplomatic engagement and de-escalation of tensions.
The timing of Bolton’s remarks is significant, as they come amid ongoing negotiations aimed at reviving the Iran nuclear deal, formally known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA). The deal, which was initially agreed upon in 2015, placed restrictions on Iran’s nuclear program in exchange for the lifting of economic sanctions. However, the U.S. withdrew from the JCPOA in 2018 under the Trump administration, and Iran has since taken steps to roll back its commitments under the agreement.
The current negotiations, involving the U.S., Iran, and other world powers, seek to restore the JCPOA and address concerns about Iran’s nuclear activities. However, significant disagreements remain, and the future of the agreement remains uncertain. Bolton has been a vocal critic of the JCPOA, arguing that it does not adequately address Iran’s nuclear ambitions and that it provides the regime with financial resources to support its destabilizing activities.
Context of U.S. Strikes and Regional Tensions
The recent U.S. strikes against Iranian-backed militias must be viewed within the context of a complex and volatile regional landscape. Iran has long been accused of supporting and arming various militant groups across the Middle East, including in Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Yemen. These groups serve as proxies for Iran, allowing it to exert influence and project power in the region without directly engaging in military conflict.
In Iraq, for example, Iran has close ties to several Shia militias that played a key role in the fight against ISIS. However, these militias have also been implicated in attacks against U.S. forces and have been accused of human rights abuses. The U.S. military presence in Iraq has been a source of friction between the two countries, with Iran calling for the withdrawal of U.S. troops.
In Syria, Iran has been a staunch supporter of the Assad regime, providing military and financial assistance throughout the country’s civil war. Iranian-backed militias have fought alongside Syrian government forces, helping to turn the tide of the conflict in Assad’s favor. The U.S. has maintained a small military presence in Syria, primarily focused on combating ISIS and preventing the resurgence of the terrorist group.
The tensions between the U.S. and Iran have also played out in the maritime domain, with several incidents involving attacks on oil tankers and other vessels in the Persian Gulf. The U.S. has accused Iran of being behind these attacks, while Iran has denied any involvement. These incidents have raised concerns about the potential for a wider conflict in the region.
Bolton’s Hard-Line Stance on Iran
John Bolton has been a consistent advocate for a hard-line stance against Iran throughout his career. As a government official and a private citizen, he has called for regime change in Iran and has supported the use of military force to prevent the country from acquiring nuclear weapons.
Bolton served as the U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations under President George W. Bush and as the National Security Advisor under President Donald Trump. In both roles, he was known for his hawkish views on foreign policy and his willingness to challenge the status quo.
As National Security Advisor, Bolton played a key role in the Trump administration’s decision to withdraw from the JCPOA. He argued that the deal was flawed and that it did not adequately address Iran’s nuclear ambitions or its support for terrorism. He also pushed for the imposition of “maximum pressure” sanctions on Iran, aimed at crippling its economy and forcing it to negotiate a new agreement.
Bolton’s views on Iran are based on his belief that the regime is inherently hostile to the U.S. and its allies. He argues that Iran is a major sponsor of terrorism and that it is actively seeking to destabilize the region. He also believes that Iran’s nuclear program poses a grave threat to international security.
Implications of Bolton’s Remarks
Bolton’s remarks about Iran being “in trouble” have several potential implications. First, they could embolden opposition groups within Iran, who may see the U.S. strikes as a sign of weakness on the part of the regime. Second, they could further escalate tensions between the U.S. and Iran, making it more difficult to reach a diplomatic solution to the nuclear issue. Finally, they could strengthen the hand of hardliners within the Iranian regime, who may argue that the U.S. is seeking to overthrow the government.
The Biden administration has sought to de-escalate tensions with Iran and revive the JCPOA. However, the U.S. has also made it clear that it will not tolerate attacks on its forces or its allies. The recent strikes against Iranian-backed militias were intended to send a message to Tehran that the U.S. is willing to use military force to protect its interests.
The future of U.S.-Iran relations remains uncertain. The two countries are deeply divided on a range of issues, and there is little trust between them. However, both sides have an interest in avoiding a wider conflict in the region. Whether they can find a way to coexist peacefully remains to be seen.
Expert Opinions and Analysis
Experts on Middle Eastern politics and international relations offer varying perspectives on the situation. Some agree with Bolton’s assessment that the Iranian regime is facing significant internal pressure and that U.S. actions can contribute to its weakening. They point to economic challenges, social unrest, and dissatisfaction with the government’s handling of various issues as evidence of the regime’s vulnerability.
Others are more cautious, arguing that the Iranian regime has proven resilient in the face of internal and external pressures. They contend that U.S. actions, while potentially deterring certain behaviors, can also backfire by strengthening the regime’s resolve and uniting hardliners against a common enemy. This perspective suggests that a more nuanced approach, combining diplomacy with targeted pressure, may be more effective in achieving U.S. objectives.
Another viewpoint emphasizes the importance of regional dynamics and the involvement of other actors in the conflict. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Israel, and Turkey have their own interests and agendas in the region, and their actions can significantly impact the situation. A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics is crucial for formulating effective policies toward Iran.
Impact on JCPOA Negotiations
Bolton’s statements also carry implications for the ongoing negotiations to revive the JCPOA. His long-standing opposition to the deal and his advocacy for a more confrontational approach could influence the dynamics of the negotiations. While the Biden administration has expressed a desire to return to the JCPOA, it faces significant challenges, including skepticism from some members of Congress and concerns about Iran’s compliance with the agreement.
Bolton’s remarks could embolden critics of the JCPOA, who argue that it is too lenient on Iran and that it does not adequately address the country’s nuclear ambitions. This could make it more difficult for the Biden administration to secure congressional support for a new agreement.
On the other hand, Bolton’s statements could also strengthen the hand of those who favor a return to the JCPOA. They may argue that the alternative to diplomacy is a more dangerous and unstable situation, with the potential for military conflict. This perspective suggests that a return to the JCPOA, even with its flaws, is the best way to prevent Iran from developing nuclear weapons.
Future Scenarios and Potential Outcomes
Several potential scenarios could unfold in the coming months and years. One possibility is that the U.S. and Iran reach an agreement to revive the JCPOA. This would require both sides to make concessions and address each other’s concerns. If successful, this could lead to a de-escalation of tensions and a period of greater stability in the region.
Another possibility is that the negotiations fail and the U.S. and Iran remain on a path of confrontation. This could lead to further escalation, with the potential for military conflict. In this scenario, the U.S. would likely continue to impose sanctions on Iran, while Iran would continue to develop its nuclear program.
A third possibility is that the situation remains in a state of limbo, with neither side willing to make the necessary concessions to reach an agreement. This could lead to a prolonged period of uncertainty and instability, with the risk of miscalculation and escalation.
The ultimate outcome will depend on a number of factors, including the political dynamics in both the U.S. and Iran, the regional security environment, and the willingness of both sides to engage in constructive diplomacy.
Detailed Look at the Targeted Militias
Understanding the groups targeted by U.S. strikes is crucial to comprehending the situation. These militias, often operating under the umbrella of the Popular Mobilization Forces (PMF) in Iraq, are complex entities. While nominally integrated into the Iraqi security forces, many maintain strong ties to Iran and operate outside of the direct control of the Iraqi government.
Kata’ib Hezbollah (KH) is one of the most prominent and powerful of these groups. It has been designated as a terrorist organization by the U.S. and has been responsible for numerous attacks on U.S. forces in Iraq. KH receives significant funding, training, and weapons from Iran and adheres to the ideology of Ayatollah Khomeini.
Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH) is another influential militia with close ties to Iran. It has also been involved in attacks on U.S. forces and has been accused of human rights abuses. AAH has a significant political wing and holds seats in the Iraqi parliament.
Other groups, such as Harakat Hezbollah al-Nujaba and Kata’ib Imam Ali, also operate within the PMF and have ties to Iran. These groups share a common goal of expelling U.S. forces from Iraq and promoting Iran’s influence in the region.
The U.S. views these militias as destabilizing forces that undermine the sovereignty of Iraq and threaten regional security. The strikes against them are intended to degrade their capabilities and deter further attacks on U.S. personnel.
The Broader Geopolitical Landscape
The U.S.-Iran conflict is not taking place in a vacuum. It is embedded within a complex geopolitical landscape involving multiple actors with competing interests. Understanding these dynamics is essential for analyzing the situation and predicting potential outcomes.
Saudi Arabia is a key player in the region and a long-time rival of Iran. The two countries have been engaged in a proxy war for years, supporting opposing sides in conflicts in Yemen, Syria, and Lebanon. Saudi Arabia views Iran’s regional ambitions as a threat to its own security and has been a strong supporter of the U.S. policy of containing Iran.
Israel is another important actor in the region and a staunch opponent of Iran. Israel views Iran’s nuclear program as an existential threat and has repeatedly threatened to take military action to prevent Iran from acquiring nuclear weapons. Israel has also been accused of carrying out covert operations against Iranian nuclear facilities and scientists.
Turkey is a regional power with its own set of interests. While Turkey has historically had close ties with the U.S., relations have become strained in recent years due to disagreements over Syria and other issues. Turkey has also sought to maintain a pragmatic relationship with Iran, despite their differences on regional issues.
Russia is another major player in the region, with a strong military presence in Syria. Russia has been a supporter of the Assad regime and has sought to expand its influence in the Middle East. Russia has also maintained a working relationship with Iran, despite its close ties with Israel.
China is increasingly playing a role in the region, driven by its growing economic interests. China is a major importer of Iranian oil and has sought to expand its economic ties with Iran, despite U.S. sanctions. China has also been a vocal critic of U.S. policy toward Iran.
The interplay of these various actors complicates the situation and makes it difficult to predict the future of U.S.-Iran relations. Any attempt to resolve the conflict must take into account the interests and concerns of all the relevant players.
Internal Dynamics within Iran
While external pressures play a significant role, understanding the internal dynamics within Iran is crucial for assessing the stability of the regime. Iranian society is characterized by a complex mix of political, economic, and social forces.
The Iranian government is a theocracy, with ultimate authority resting in the hands of the Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. The Supreme Leader controls the military, the judiciary, and the state-owned media. He also has significant influence over economic policy.
The Iranian government faces a number of challenges, including a struggling economy, high unemployment, and widespread corruption. These challenges have led to social unrest and protests in recent years.
There are also divisions within the Iranian political establishment. Some factions favor a more pragmatic approach to foreign policy and economic reform, while others advocate for a more hard-line stance. These divisions can complicate decision-making and make it difficult to implement effective policies.
The level of popular support for the Iranian government is difficult to gauge. There are no free and fair elections in Iran, and the government tightly controls the media and suppresses dissent. However, it is clear that there is widespread dissatisfaction with the government’s performance.
The Iranian regime has proven resilient in the face of internal and external pressures. However, the combination of economic challenges, social unrest, and political divisions could eventually weaken the regime and create opportunities for change.
Conclusion: A Precarious Situation
John Bolton’s assessment that Iran is “in trouble” reflects a widely held view among those who advocate for a more assertive approach to the country. However, it is important to recognize that the situation is complex and that there are no easy solutions.
The U.S. faces a difficult balancing act in its policy toward Iran. On the one hand, it must deter Iran from engaging in destabilizing activities and prevent it from acquiring nuclear weapons. On the other hand, it must avoid escalating tensions and provoking a wider conflict in the region.
The path forward requires a combination of diplomacy, targeted pressure, and a clear understanding of the regional dynamics. The U.S. must work with its allies to contain Iran’s influence and promote stability in the Middle East. It must also be prepared to engage in direct talks with Iran, if necessary, to address the nuclear issue and de-escalate tensions.
The future of U.S.-Iran relations remains uncertain. However, the stakes are high, and it is essential that the U.S. pursues a policy that protects its interests and promotes peace and security in the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What was the main point of John Bolton’s statement regarding Iran?
John Bolton stated that Iran is “in trouble” and its regime is weakening following recent U.S. military strikes against Iranian-backed militias in Syria and Iraq. He believes these strikes demonstrate U.S. resolve and could destabilize the Iranian government.
2. What was the U.S. response that triggered Bolton’s commentary?
The U.S. military strikes in Syria and Iraq, targeting Iranian-backed militias, prompted Bolton’s comments. These strikes were in response to attacks on U.S. forces stationed in the region.
3. What is Bolton’s general stance on U.S. policy toward Iran?
Bolton has consistently advocated for a hard-line approach toward Iran, including regime change and the use of military force to prevent the country from acquiring nuclear weapons. He is a vocal critic of the Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA).
4. How might Bolton’s remarks affect negotiations around the Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA)?
Bolton’s remarks could embolden critics of the JCPOA and make it more difficult for the Biden administration to secure congressional support for a new agreement. Conversely, some may argue that his hawkish views highlight the need for the JCPOA to prevent further escalation.
5. What are some of the internal challenges facing the Iranian regime, as suggested by analysts?
Analysts point to economic challenges, social unrest, and dissatisfaction with the government’s handling of various issues as internal challenges facing the Iranian regime. These factors, combined with external pressures, could potentially weaken the regime.