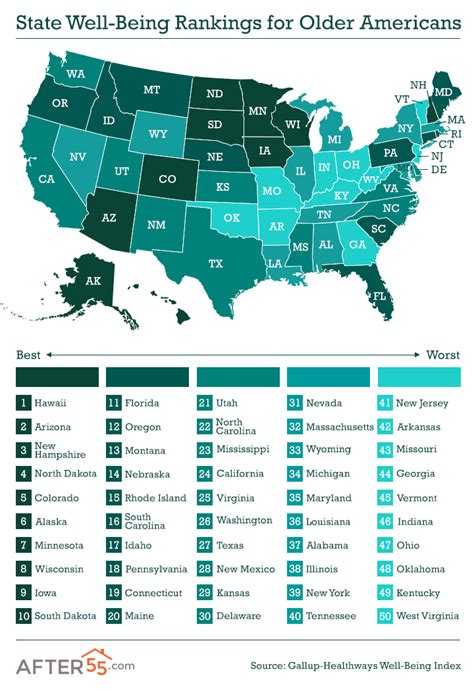
Happiest seniors reside in Hawaii, followed by Maryland, Maine, Iowa, and South Dakota, according to a recent Gallup-Sharecare survey analyzing well-being across all 50 states. The data, reflecting responses collected throughout 2023, examined key elements such as physical health, community ties, financial security, purpose, and social relationships to determine the states where older Americans thrive most.
Hawaii clinched the top spot, demonstrating the highest overall well-being among its senior population. Maryland secured second place, followed by Maine, Iowa, and South Dakota, which rounded out the top five. These states scored favorably across the five elements of well-being measured in the study.
The Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index, a comprehensive measure, assesses how people experience their daily lives and provides insights into community health and quality of life. For older adults, this index becomes particularly relevant, highlighting the factors that contribute to a fulfilling and healthy later life. The five elements—purpose, social relationships, financial security, community, and physical health—are interconnected and contribute significantly to an individual’s overall well-being.
“These elements are not independent; they influence each other,” explains Dr. Lotte Dyrbye, Sharecare’s Chief Medical Officer, in an interview. “For example, someone with a strong sense of purpose may be more likely to engage in physical activity and maintain social connections, further enhancing their well-being.”
The report highlighted that states with strong social infrastructure, access to healthcare, and opportunities for community involvement tend to rank higher in overall well-being for older adults. Financial stability also plays a crucial role, allowing seniors to afford healthcare, housing, and other essential needs without undue stress.
While the top five states demonstrated exceptional performance, the survey also identified areas where states could improve to better support their aging populations. These areas often involve addressing social isolation, improving access to affordable healthcare, and creating age-friendly communities that promote physical activity and social engagement. The data suggests that targeted interventions focusing on these key areas can significantly enhance the quality of life for older adults across the nation.
Further analysis of the data reveals some common themes among the top-ranked states. Hawaii, for instance, boasts a climate conducive to outdoor activities, strong community bonds, and a culture that values family and social connections. Maryland benefits from its proximity to major healthcare facilities and a relatively high median income, which contributes to financial stability for many seniors. Maine’s picturesque landscapes and strong sense of community also contribute to its high ranking, offering opportunities for outdoor recreation and social engagement. Iowa’s affordable cost of living and strong social support networks make it an attractive place for seniors to retire, while South Dakota’s low crime rate and access to healthcare contribute to a sense of security and well-being among its older population.
The Gallup-Sharecare survey serves as a valuable resource for policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations seeking to improve the lives of older Americans. By understanding the factors that contribute to well-being in later life, stakeholders can develop targeted interventions and programs that address the specific needs of their aging populations. This ultimately contributes to creating a society that supports and empowers older adults to live fulfilling and healthy lives.
Diving Deeper into the Five Elements of Well-Being:
The Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index evaluates five key elements that significantly influence an individual’s overall quality of life, especially during the senior years. Understanding these elements in detail provides valuable insights into the specific areas where states excel and where improvements can be made.
-
Purpose: This element refers to having a sense of meaning and direction in life. It encompasses feeling motivated, engaged, and connected to something larger than oneself. For seniors, purpose can come from various sources, such as volunteering, pursuing hobbies, spending time with family, or continuing to learn and grow. States that foster a sense of purpose among their older adults often have robust volunteer opportunities, lifelong learning programs, and community initiatives that encourage engagement. A lack of purpose can lead to feelings of isolation, depression, and a decline in overall well-being.
-
Social Relationships: Strong social connections are essential for maintaining mental and emotional health, particularly as individuals age. Social relationships encompass connections with family, friends, neighbors, and community members. These relationships provide support, companionship, and a sense of belonging. States that prioritize social connections for seniors often have senior centers, community events, and programs that facilitate social interaction. Conversely, social isolation can have detrimental effects on health, including increased risk of cognitive decline, depression, and even physical illness.
-
Financial Security: Financial stability plays a crucial role in ensuring that seniors can afford basic necessities, such as housing, food, and healthcare. It also provides a sense of security and peace of mind. States that prioritize financial security for seniors often have programs that help them manage their finances, access affordable healthcare, and find affordable housing options. Financial stress can have a significant impact on mental and physical health, leading to anxiety, depression, and chronic health problems.
-
Community: This element refers to the sense of belonging and connection to the community in which one lives. It encompasses feeling safe, supported, and valued by one’s neighbors and community members. States that foster a strong sense of community often have vibrant local businesses, community events, and opportunities for civic engagement. A strong community can provide a sense of belonging and support, which is especially important for seniors who may be experiencing social isolation or loneliness.
-
Physical Health: Maintaining physical health is essential for seniors to remain independent and active. This element encompasses factors such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and access to quality healthcare. States that prioritize physical health for seniors often have programs that promote physical activity, healthy eating, and access to preventive healthcare services. Good physical health can improve mobility, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and enhance overall quality of life.
State-Specific Examples and Insights:
To gain a more nuanced understanding of the factors contributing to senior well-being, it’s helpful to examine specific examples from the top-ranked states.
-
Hawaii: Hawaii’s consistently high ranking in well-being surveys is often attributed to its strong sense of community, cultural emphasis on family and social connections, and a climate conducive to outdoor activities. The state also boasts a relatively high life expectancy, which suggests that its residents are living longer and healthier lives. However, the high cost of living in Hawaii can be a challenge for some seniors, particularly those on fixed incomes.
-
Maryland: Maryland benefits from its proximity to major healthcare facilities, a relatively high median income, and a diverse range of cultural and recreational opportunities. The state also has a strong network of senior centers and community organizations that provide support and services to older adults. However, Maryland’s high cost of living and traffic congestion can be challenges for some seniors.
-
Maine: Maine’s picturesque landscapes, strong sense of community, and low crime rate make it an attractive place for seniors to retire. The state also has a growing number of age-friendly communities that are designed to meet the needs of older adults. However, Maine’s cold winters and limited job opportunities can be challenges for some seniors.
-
Iowa: Iowa’s affordable cost of living, strong social support networks, and access to quality healthcare make it an attractive place for seniors to retire. The state also has a large number of small towns and rural communities that offer a sense of peace and tranquility. However, Iowa’s limited public transportation options and lack of diversity can be challenges for some seniors.
-
South Dakota: South Dakota’s low crime rate, access to healthcare, and affordable cost of living contribute to a sense of security and well-being among its older population. The state also has a strong sense of community and a rich cultural heritage. However, South Dakota’s harsh winters and limited job opportunities can be challenges for some seniors.
Addressing Challenges and Improving Well-Being:
While the top-ranked states offer valuable insights into what contributes to senior well-being, it’s important to acknowledge that challenges remain, even in these states. These challenges include:
-
Social Isolation: Social isolation is a growing problem among seniors, particularly those who live alone or have limited mobility. It can lead to feelings of loneliness, depression, and cognitive decline. Addressing social isolation requires a multi-pronged approach that includes providing opportunities for social interaction, promoting community engagement, and offering support services to isolated seniors.
-
Access to Affordable Healthcare: Healthcare costs continue to rise, making it increasingly difficult for seniors to afford the care they need. This can lead to delays in seeking treatment, which can have serious consequences for their health. Addressing this challenge requires expanding access to affordable healthcare options, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and promoting preventive care services.
-
Age-Friendly Communities: Age-friendly communities are designed to meet the needs of older adults, making it easier for them to live independently and participate fully in community life. These communities typically have features such as accessible transportation, safe streets, and affordable housing. Creating age-friendly communities requires a collaborative effort involving government agencies, community organizations, and residents.
-
Financial Security: Many seniors struggle to make ends meet on fixed incomes, particularly with rising housing costs and inflation. This can lead to stress, anxiety, and difficulty affording basic necessities. Addressing this challenge requires providing financial assistance to low-income seniors, such as through Social Security and Supplemental Security Income (SSI), and promoting financial literacy programs.
-
Caregiving Support: Many seniors rely on family members or other caregivers for assistance with daily tasks. However, caregiving can be a demanding and stressful role, and caregivers often need support to avoid burnout. Providing support to caregivers requires offering respite care services, providing education and training, and connecting caregivers with support groups.
The Role of Policy and Community Initiatives:
Addressing these challenges and improving the well-being of older Americans requires a concerted effort from policymakers, healthcare providers, community organizations, and individuals. Some key policy and community initiatives that can make a difference include:
-
Expanding Access to Affordable Healthcare: Policymakers can expand access to affordable healthcare by increasing funding for Medicare and Medicaid, promoting the use of preventive care services, and negotiating lower drug prices.
-
Creating Age-Friendly Communities: Policymakers and community organizations can create age-friendly communities by investing in accessible transportation, promoting safe streets, and developing affordable housing options.
-
Combating Social Isolation: Community organizations can combat social isolation by offering programs that promote social interaction, such as senior centers, volunteer opportunities, and community events.
-
Providing Financial Assistance to Low-Income Seniors: Policymakers can provide financial assistance to low-income seniors through Social Security, Supplemental Security Income (SSI), and other programs.
-
Supporting Caregivers: Healthcare providers and community organizations can support caregivers by offering respite care services, providing education and training, and connecting caregivers with support groups.
Conclusion:
The Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index provides valuable insights into the factors that contribute to the well-being of older Americans. While some states are doing exceptionally well in supporting their aging populations, challenges remain, and there is room for improvement in all states. By understanding the specific needs of older adults and implementing targeted interventions, policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations can work together to create a society that supports and empowers older adults to live fulfilling and healthy lives. This includes focusing on the five key elements of well-being: purpose, social relationships, financial security, community, and physical health. By prioritizing these elements, we can ensure that all older Americans have the opportunity to thrive in their later years. The data serves as a call to action, urging states and communities to proactively address the challenges facing seniors and to invest in programs and policies that promote their well-being. Ultimately, creating a society that values and supports its older citizens is not only the right thing to do, but also benefits society as a whole. A thriving senior population contributes to the economy, strengthens communities, and enriches the lives of all.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
-
What is the Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index?
The Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index is a comprehensive measure that assesses how people experience their daily lives. It provides insights into community health and quality of life, focusing on five key elements: purpose, social relationships, financial security, community, and physical health. The index is based on data collected through surveys and interviews with individuals across the United States.
-
What are the five elements of well-being measured in the Gallup-Sharecare survey?
The five elements of well-being are:
- Purpose: Having a sense of meaning and direction in life.
- Social Relationships: Having strong and supportive relationships with family, friends, and community members.
- Financial Security: Having financial stability and the ability to meet basic needs.
- Community: Having a sense of belonging and connection to the community.
- Physical Health: Maintaining good physical health through regular exercise, healthy eating, and access to quality healthcare.
-
Which states ranked highest in well-being for seniors in 2023, according to the Gallup-Sharecare survey?
The top five states for senior well-being in 2023 were:
- Hawaii
- Maryland
- Maine
- Iowa
- South Dakota
-
Why is well-being important for older adults?
Well-being is crucial for older adults as it directly impacts their quality of life, physical health, mental health, and overall sense of fulfillment. High levels of well-being are associated with greater independence, reduced risk of chronic diseases, increased social engagement, and a longer lifespan. Focusing on well-being helps older adults remain active, connected, and engaged in their communities.
-
What can states and communities do to improve the well-being of their senior populations?
States and communities can take several steps to enhance senior well-being, including:
- Expanding access to affordable healthcare and preventive services.
- Creating age-friendly communities with accessible transportation, safe streets, and affordable housing.
- Combating social isolation by offering programs that promote social interaction and community engagement.
- Providing financial assistance to low-income seniors through programs like Social Security and SSI.
- Supporting caregivers by offering respite care services, education, and support groups.
- Promoting lifelong learning opportunities and volunteer programs that provide seniors with a sense of purpose.
- Encouraging physical activity and healthy eating through community-based programs and initiatives.
-
What factors contribute to Hawaii’s high ranking in senior well-being?
Hawaii’s high ranking is attributed to its strong sense of community, cultural emphasis on family and social connections, a climate conducive to outdoor activities, and a relatively high life expectancy. However, the high cost of living can be a challenge for some seniors.
-
How does financial security impact the well-being of older adults?
Financial security is essential for ensuring that seniors can afford basic necessities like housing, food, and healthcare. It also provides a sense of security and peace of mind, reducing stress and anxiety. Financial stress can have a significant impact on mental and physical health, leading to depression and chronic health problems.
-
What are some of the challenges facing seniors in maintaining their well-being?
Some key challenges include:
- Social isolation and loneliness
- Rising healthcare costs and limited access to affordable care
- Lack of age-friendly communities with accessible transportation and housing
- Financial insecurity due to fixed incomes and rising expenses
- Caregiving responsibilities for family members or spouses
-
How can families and individuals support the well-being of older adults in their lives?
Families and individuals can support senior well-being by:
- Maintaining regular contact and providing companionship
- Assisting with transportation and errands
- Encouraging participation in social activities and community events
- Helping with household tasks and yard work
- Providing financial support if possible
- Advocating for their needs and rights
- Ensuring they have access to healthcare and other essential services
-
Why is the concept of “purpose” so important for senior well-being?
Having a sense of purpose gives older adults a reason to get up in the morning, stay engaged in life, and maintain a positive outlook. Purpose can come from various sources, such as volunteering, pursuing hobbies, spending time with family, or continuing to learn and grow. A lack of purpose can lead to feelings of isolation, depression, and a decline in overall well-being.
-
What kind of community programs can foster better social relationships for seniors?
Community programs that can improve social relationships for seniors include: senior centers offering various activities and social gatherings, volunteer opportunities providing a chance to connect with others while contributing to the community, intergenerational programs linking seniors with younger generations, group fitness classes promoting social interaction and physical health, and book clubs or hobby groups fostering shared interests and discussions.
-
Are there specific policies related to the Elderly that might have an impact on the survey?
Yes, policies such as Social Security benefits, Medicare and Medicaid coverage, affordable housing initiatives for seniors, transportation assistance programs, and elder abuse prevention laws can significantly influence the well-being of older adults and, consequently, their responses in well-being surveys. These policies affect financial security, access to healthcare, safety, and overall quality of life.
-
How does the physical environment of a state impact the well-being of its senior residents?
The physical environment significantly impacts senior well-being. Factors like air and water quality affect respiratory and overall health. Access to green spaces and parks promotes physical activity and mental well-being. Safe and accessible infrastructure, including well-maintained sidewalks and public transportation, allows seniors to remain active and engaged in their communities. Climate and weather patterns can also influence outdoor activities and social interactions.
-
Can lifestyle changes actually improve older adults’ happiness and well-being? What are some specific examples?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly improve older adults’ happiness and well-being. Examples include: Engaging in regular physical activity like walking, swimming, or yoga to boost mood and physical health; adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to enhance energy levels and prevent chronic diseases; joining social clubs or volunteering to combat loneliness and foster a sense of purpose; learning new skills or pursuing hobbies to stimulate the mind and maintain cognitive function; and practicing mindfulness or meditation to reduce stress and improve emotional well-being.
-
What are some indicators to show if senior citizens lack financial security in a given state?
Indicators of financial insecurity among senior citizens in a state may include: A high percentage of seniors relying solely on Social Security for income; significant numbers eligible for or receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI); observable difficulties affording housing, healthcare, or food; disproportionately high rates experiencing homelessness or housing instability; an increase in seniors seeking assistance from food banks and social services; and a noticeable decline in discretionary spending or participation in recreational activities.
-
Are there any specific types of communities or neighborhoods that are known to be better for senior well-being?
Age-friendly communities, specifically designed with the needs of older adults in mind, are known to be better for senior well-being. These communities often feature accessible housing, walkable streets, convenient transportation options, readily available healthcare services, social and recreational activities, and opportunities for civic engagement. Neighborhoods with strong social networks, active community centers, and low crime rates also contribute positively to the well-being of senior residents.
-
How is “community” as defined in the survey different from “social relationships”?
In the context of the survey, “social relationships” refer to the quality and strength of personal connections with family, friends, and close acquaintances. It focuses on the individual’s support network and the depth of their interpersonal bonds. “Community,” on the other hand, encompasses a broader sense of belonging and connection to the wider locality or region, including feeling safe, supported, and valued by the neighborhood, town, or city in which one lives. It reflects engagement and participation in local activities and institutions.
-
Does the Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index account for cultural differences between states when assessing senior happiness?
While the Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index aims to provide a standardized measure of well-being across all states, it’s essential to acknowledge that cultural differences can influence how individuals perceive and report their own well-being. Certain cultural values or norms may prioritize different aspects of life, such as family connections, community involvement, or individual achievement, which can shape responses to survey questions related to the five elements of well-being. However, the index strives for neutrality and attempts to capture universally valued dimensions of well-being, such as health, security, and purpose.
-
What are some limitations of using a survey like the Gallup-Sharecare Well-Being Index to determine the “happiest” states for seniors?
Limitations include: Response bias, where individuals may provide socially desirable answers; sampling bias, if the survey doesn’t accurately represent the senior population in each state; subjectivity in interpreting well-being, as cultural and personal factors vary; reliance on self-reported data, which may not always reflect actual experiences; and the inability to capture the full complexity of individual circumstances impacting happiness. Additionally, the survey provides a snapshot in time and may not account for changes in well-being over time.
-
What should be the next steps to be taken after these results of the survey are released? Next steps should involve: Analyzing detailed data to identify specific areas of strength and weakness in each state; using findings to inform policy changes and community initiatives aimed at improving senior well-being; allocating resources to address areas where seniors are struggling; collaborating with healthcare providers, community organizations, and senior advocacy groups to develop targeted interventions; conducting further research to explore underlying factors contributing to well-being disparities; and regularly monitoring and evaluating progress to ensure initiatives are effective and responsive to the evolving needs of older adults.









