Lynas Rare Earths has achieved a milestone, becoming the first company outside of China to commercially produce separated rare earth oxides at scale, marking a significant shift in the global rare earth supply chain.
Lynas Rare Earths, an Australian company, has commenced production at its Kalgoorlie Rare Earths Processing Facility in Western Australia, breaking China’s near-monopoly on separated rare earth oxides production. This achievement is viewed as a crucial step towards diversifying the global supply chain of these critical minerals, essential for various high-tech applications including electric vehicles, wind turbines, and electronics. The company officially announced the start of production in late May 2024. The Kalgoorlie facility will process rare earth concentrate from Lynas’s Mt Weld mine, also located in Western Australia.
“We are delighted to announce that our Kalgoorlie Rare Earths Processing Facility is now in production,” said Amanda Lacaze, CEO of Lynas Rare Earths. “This is a significant achievement for Lynas and for Australia, and it marks a key step in our strategy to provide responsibly sourced rare earth materials to meet growing global demand.”
The operational commencement of the Kalgoorlie facility not only diversifies the rare earth supply chain but also bolsters Australia’s position as a critical minerals hub. Rare earth elements (REEs) are a set of seventeen metallic elements that are vital in numerous modern technologies. China has historically dominated the rare earth market, controlling both mining and processing operations, which has raised concerns about supply security among Western nations.
The establishment of the Kalgoorlie plant has been hailed as a strategic move to counter this reliance on China. The facility aims to produce approximately 9,000 tonnes per annum (tpa) of rare earth oxides, significantly increasing the availability of these materials from outside China. This production capacity will contribute to satisfying the rising demand driven by the global transition to green energy and advanced technology.
The development of the Kalgoorlie facility has been supported by both public and private investment. The Australian government has recognized the importance of securing rare earth supplies and has provided financial backing for the project. The facility represents a substantial investment in Australia’s critical minerals sector, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth in the region.
Strategic Implications and Geopolitical Context
The geopolitical implications of Lynas’ achievement are profound. Rare earth elements are at the heart of many advanced technologies, including defense systems, renewable energy infrastructure, and consumer electronics. China’s dominance in the rare earth market has allowed it to exert considerable influence over global supply chains.
The commissioning of the Kalgoorlie facility is seen as a strategic move to reduce dependence on China and enhance supply chain resilience. Western governments, including the United States and Australia, have been actively seeking to diversify their sources of critical minerals to mitigate potential risks associated with relying on a single supplier.
The U.S. Department of Defense has also taken steps to support the development of rare earth processing capabilities within the United States and allied nations. This support reflects the growing recognition of the strategic importance of rare earth elements in maintaining technological and military superiority.
Technical Overview of the Kalgoorlie Facility
The Kalgoorlie Rare Earths Processing Facility is designed to process rare earth concentrate from the Mt Weld mine, which is known for its high-grade rare earth deposits. The processing involves several stages, including cracking, leaching, and separation.
The cracking and leaching stages involve breaking down the mineral concentrate and dissolving the rare earth elements into a solution. The separation stage is the most complex and technologically advanced part of the process, where individual rare earth elements are separated from each other. This is typically achieved using solvent extraction techniques.
The separated rare earth oxides are then dried and packaged for sale to manufacturers around the world. The Kalgoorlie facility incorporates state-of-the-art technology and adheres to strict environmental standards. Lynas Rare Earths is committed to sustainable and responsible mining and processing practices.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Lynas Rare Earths emphasizes its commitment to environmental sustainability and responsible mining practices. The company has implemented various measures to minimize the environmental impact of its operations. These measures include water management, waste reduction, and rehabilitation of mined areas.
The Kalgoorlie facility is designed to operate with a focus on minimizing water usage and maximizing recycling. Lynas has invested in advanced water treatment technologies to ensure that water discharged from the facility meets stringent environmental standards.
The company also works closely with local communities to address any concerns and ensure that its operations benefit the local economy. Lynas is committed to transparency and open communication with stakeholders.
Market Dynamics and Future Outlook
The global rare earth market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles, wind turbines, and other green technologies. The transition to a low-carbon economy is fueling the demand for rare earth elements, which are essential components in these technologies.
The commissioning of the Kalgoorlie facility will help to meet this growing demand and reduce the risk of supply shortages. Lynas Rare Earths is well-positioned to capitalize on the growing market for rare earth elements.
The company has plans to further expand its production capacity in the future. Lynas is also exploring opportunities to develop new rare earth deposits in Australia and other countries.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Lynas Rare Earths has achieved a significant milestone, the company faces several challenges. One of the main challenges is competition from China, which remains the dominant player in the rare earth market.
China has a well-established rare earth industry with extensive infrastructure and lower production costs. Lynas will need to continue to innovate and improve its efficiency to compete effectively with Chinese producers.
Another challenge is the environmental and social concerns associated with rare earth mining and processing. Lynas will need to maintain its commitment to sustainable and responsible practices to address these concerns and maintain its social license to operate.
Despite these challenges, Lynas Rare Earths has significant opportunities for growth. The growing demand for rare earth elements, combined with the desire of Western governments to diversify their supply chains, creates a favorable environment for Lynas.
The company’s strong financial position, its high-grade rare earth deposits, and its commitment to innovation position it well for future success.
Industry Reactions and Expert Opinions
Industry analysts and experts have hailed the commissioning of the Kalgoorlie facility as a major step forward for the rare earth industry. They believe that it will help to reduce dependence on China and create a more resilient global supply chain.
“The start of production at the Kalgoorlie facility is a game-changer for the rare earth industry,” said Dr. Alan Bye, a leading expert in rare earth metallurgy. “It demonstrates that it is possible to produce separated rare earth oxides outside of China on a commercial scale.”
Other experts have emphasized the strategic importance of the Kalgoorlie facility. “This facility is a critical asset for Australia and for the Western world,” said Professor Gavin Mudd, an expert in environmental engineering at RMIT University. “It will help to ensure that we have access to the rare earth elements that we need for our economy and our security.”
Further Expansion and Development
Lynas Rare Earths is not resting on its laurels. The company has ambitious plans for further expansion and development. These plans include increasing production capacity at the Mt Weld mine and developing new rare earth deposits in Australia and other countries.
Lynas is also investing in research and development to improve its processing technologies and reduce its environmental impact. The company is committed to being a leader in sustainable and responsible rare earth production.
Impact on Local Communities
The development of the Kalgoorlie facility has had a positive impact on local communities in Western Australia. The project has created hundreds of jobs and has stimulated economic growth in the region.
Lynas Rare Earths is committed to working closely with local communities to ensure that its operations benefit the local economy and environment. The company has established community consultation forums and has invested in local infrastructure projects.
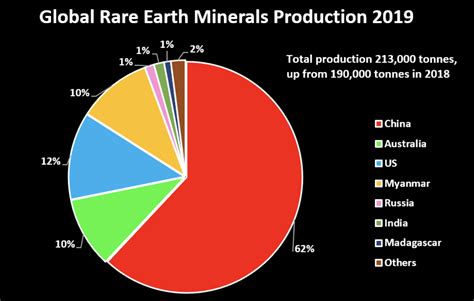
Global Rare Earth Reserves and Production
While China holds significant rare earth reserves, other countries, including Australia, the United States, Brazil, and India, also possess substantial deposits. However, the key differentiator has been China’s dominance in processing capabilities. This dominance stems from a combination of factors, including lower labor costs, less stringent environmental regulations (historically), and government support for the industry.
The U.S. Geological Survey estimates that China holds approximately 35% of the world’s rare earth reserves, followed by Vietnam (18%), Brazil (18%), and Russia (10%). Australia holds around 4% of the global reserves. Despite not holding the largest share of reserves, Australia is becoming a significant player due to its commitment to developing a complete supply chain, from mining to processing.
Technological Advancements in Rare Earth Processing
Rare earth processing involves complex chemical processes to separate the individual elements from the ore. Solvent extraction is the most common method used, but it is energy-intensive and can generate significant waste.
Researchers and companies are exploring new technologies to improve the efficiency and sustainability of rare earth processing. These technologies include:
- Ion exchange: This method uses resins to selectively absorb rare earth ions from solution. It is more energy-efficient than solvent extraction and generates less waste.
- Membrane separation: This method uses membranes to separate rare earth ions based on their size and charge. It is a promising technology for recovering rare earth elements from electronic waste.
- Direct extraction: This method involves extracting rare earth elements directly from the ore without the need for pre-treatment. It has the potential to significantly reduce processing costs and environmental impact.
The Role of Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the rare earth industry. Governments can support the development of domestic rare earth industries through:
- Funding research and development: Governments can fund research into new rare earth processing technologies and support the development of domestic rare earth resources.
- Providing financial incentives: Governments can provide financial incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies, to encourage companies to invest in rare earth mining and processing.
- Setting environmental standards: Governments can set environmental standards for rare earth mining and processing to ensure that these activities are carried out in a sustainable manner.
- Establishing strategic stockpiles: Governments can establish strategic stockpiles of rare earth elements to ensure that they have access to these materials in times of crisis.
The Impact of Geopolitical Tensions
Geopolitical tensions have a significant impact on the rare earth market. Concerns about China’s dominance in the rare earth market have led Western governments to seek to diversify their supply chains.
The trade war between the United States and China has further highlighted the importance of rare earth elements. The United States has imposed tariffs on Chinese rare earth imports, and China has threatened to restrict rare earth exports to the United States.
These tensions have created opportunities for companies like Lynas Rare Earths, which are able to supply rare earth elements from outside of China.
Rare Earth Elements and Green Technologies
Rare earth elements are essential components in many green technologies, including:
- Electric vehicles: Rare earth magnets are used in electric vehicle motors.
- Wind turbines: Rare earth magnets are used in wind turbine generators.
- Solar panels: Rare earth elements are used in some types of solar panels.
- Energy-efficient lighting: Rare earth elements are used in energy-efficient light bulbs.
The growing demand for green technologies is driving the demand for rare earth elements. As the world transitions to a low-carbon economy, the demand for rare earth elements is expected to continue to grow.
The Future of the Rare Earth Industry
The future of the rare earth industry is uncertain, but several trends are likely to shape its development:
- Increased demand: The demand for rare earth elements is expected to continue to grow, driven by the increasing demand for green technologies.
- Diversification of supply: Western governments will continue to seek to diversify their supply chains to reduce dependence on China.
- Technological innovation: Companies will continue to invest in research and development to improve the efficiency and sustainability of rare earth processing.
- Geopolitical tensions: Geopolitical tensions will continue to influence the rare earth market.
Lynas Rare Earths is well-positioned to capitalize on these trends. The company’s strong financial position, its high-grade rare earth deposits, and its commitment to innovation position it well for future success. The start of production at the Kalgoorlie facility is a major step forward for the company and for the rare earth industry as a whole. This marks a new chapter, where a diversified and resilient supply chain will be critical for future technological advancements and energy security.
The Role of Recycling
Recycling of rare earth elements from electronic waste and end-of-life products is gaining increasing attention as a means to supplement primary mining and reduce environmental impacts. Electronic waste, such as discarded smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices, contains valuable rare earth elements that can be recovered and reused.
Several companies and research institutions are developing technologies to efficiently extract rare earth elements from electronic waste. These technologies include hydrometallurgical processes, pyrometallurgical processes, and bioleaching.
Recycling rare earth elements can help to reduce the demand for primary mining, conserve resources, and minimize environmental pollution. However, the recycling of rare earth elements is still in its early stages of development and faces several challenges, including the complex composition of electronic waste, the low concentration of rare earth elements in some waste streams, and the cost of recycling.
The Significance of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Factors
ESG factors are becoming increasingly important in the rare earth industry. Investors, customers, and other stakeholders are demanding that companies operate in a sustainable and responsible manner.
Companies are increasingly being evaluated on their ESG performance, and those with strong ESG credentials are more likely to attract investment and secure contracts.
ESG factors in the rare earth industry include:
- Environmental: Minimizing environmental impact, reducing waste, conserving water, and rehabilitating mined areas.
- Social: Protecting the rights of workers, engaging with local communities, and promoting social and economic development.
- Governance: Ensuring transparency, accountability, and ethical business practices.
Lynas Rare Earths has made a commitment to sustainability and responsible mining practices. The company has implemented various measures to minimize the environmental impact of its operations and to engage with local communities.
The Critical Importance of Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
In an era where ethical sourcing and supply chain integrity are paramount, traceability and transparency have emerged as critical factors in the rare earth industry. Consumers, manufacturers, and governments are increasingly demanding visibility into the origin and processing of rare earth elements to ensure they are not contributing to environmental damage, human rights abuses, or conflict financing.
Traceability refers to the ability to track the movement of rare earth elements from the mine to the end product, while transparency involves the disclosure of information about the sourcing, processing, and environmental impact of rare earth production.
Blockchain technology is being explored as a potential solution for enhancing traceability and transparency in the rare earth supply chain. Blockchain is a decentralized, immutable ledger that can be used to record and track transactions in a secure and transparent manner.
By using blockchain technology, companies can create a digital record of the origin, processing, and movement of rare earth elements, allowing stakeholders to verify the authenticity and sustainability of the supply chain.
The Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for ensuring a sustainable and responsible rare earth industry. Governments, companies, and research institutions need to work together to address the challenges facing the industry and to promote best practices.
International cooperation can take several forms, including:
- Sharing information and best practices: Governments and companies can share information about rare earth resources, processing technologies, and environmental regulations.
- Developing international standards: Governments and industry organizations can work together to develop international standards for rare earth mining and processing.
- Supporting research and development: Governments can jointly fund research into new rare earth processing technologies and support the development of domestic rare earth resources.
- Promoting responsible sourcing: Governments and companies can work together to promote responsible sourcing of rare earth elements and to combat illegal mining and trafficking.
The establishment of the Kalgoorlie facility is a testament to the benefits of international cooperation. The project has been supported by both the Australian government and private investors, and it has involved collaboration with companies and research institutions from around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why is Lynas’s Kalgoorlie facility significant?
Lynas’s Kalgoorlie facility is significant because it’s the first large-scale rare earth separation plant outside of China. This diversifies the global supply chain, reducing reliance on a single country for these critical minerals, which are essential for various high-tech applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies. It also enhances Australia’s position as a key player in the critical minerals sector.
2. What are rare earth elements, and why are they important?
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a set of 17 metallic elements vital for numerous modern technologies. They are used in electric vehicle motors, wind turbines, smartphones, defense systems, and many other high-tech applications. Their unique properties make them irreplaceable in many of these applications.
3. How much rare earth oxide does the Kalgoorlie facility aim to produce annually?
The Kalgoorlie facility aims to produce approximately 9,000 tonnes per annum (tpa) of rare earth oxides. This will significantly increase the availability of these materials from outside China and help meet the growing global demand.
4. What are the environmental considerations for rare earth processing, and how does Lynas address them?
Rare earth processing can have environmental impacts, including water usage, waste generation, and potential pollution. Lynas addresses these concerns by implementing measures such as advanced water treatment technologies to minimize water usage and maximize recycling, adhering to strict environmental standards, and working closely with local communities to address concerns. They also focus on rehabilitating mined areas and promoting transparency in their operations.
5. What are the geopolitical implications of this facility’s operation?
The operation of the Kalgoorlie facility has significant geopolitical implications. It reduces the dependence of Western nations on China for rare earth elements, enhancing supply chain resilience and reducing the potential for China to exert undue influence through its dominance in the rare earth market. This diversification is seen as crucial for maintaining technological and military superiority and securing access to these critical minerals for strategic purposes.