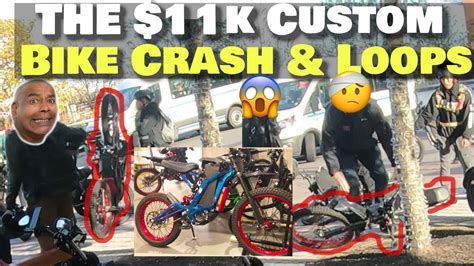
Hundreds of confiscated e-bikes and scooters were crushed in Staten Island, New York, sparking debate over the city’s approach to enforcing regulations on the increasingly popular, yet often illegally operated, vehicles. The dramatic demonstration, orchestrated by city officials, aimed to highlight the dangers and prevalence of unregistered and non-compliant e-bikes and scooters, but critics argue it represents a wasteful and ineffective solution to a complex transportation challenge.
The destruction, captured in a video that circulated widely online, showed heavy machinery methodically dismantling the seized vehicles. According to the New York City Department of Transportation (NYCDOT), the crushed e-bikes and scooters were confiscated due to various violations, including illegal modifications, lack of proper registration, and operation in restricted areas. City officials maintain that the crackdown is essential for public safety, citing concerns about reckless riding, sidewalk congestion, and the potential for battery fires. “These e-bikes…are not only a nuisance, but they are dangerous,” said one official involved in the operation.
However, the large-scale destruction has drawn criticism from advocacy groups and some residents who argue that the city’s resources could be better used to create safer infrastructure for e-bikes and scooters, as well as to educate riders and enforce existing regulations more effectively. Critics contend that simply crushing the vehicles does little to address the root causes of illegal operation and may disproportionately affect low-income workers who rely on e-bikes for transportation and delivery services.
The debate surrounding e-bike and scooter regulation in New York City reflects a broader challenge facing urban areas across the country as they grapple with the rise of micromobility. While these vehicles offer a convenient and environmentally friendly alternative to cars, their widespread adoption has also raised concerns about safety, traffic management, and equitable access. The Staten Island crackdown underscores the tension between the city’s efforts to maintain order and the need to accommodate new forms of transportation in a rapidly evolving urban landscape.
The NYCDOT has been actively working to implement a comprehensive e-bike and scooter program, which includes designated bike lanes, parking regulations, and safety education initiatives. However, the pace of these efforts has been criticized as too slow, and many argue that more needs to be done to create a safe and sustainable environment for micromobility in the city. The destruction of the confiscated vehicles has reignited the debate over the best approach to regulating e-bikes and scooters, with some calling for a more nuanced and collaborative solution that balances enforcement with education and infrastructure development.
The surge in e-bike and scooter usage in New York City can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing cost of traditional transportation, the growing demand for food and package delivery services, and the desire for more sustainable commuting options. E-bikes and scooters offer a convenient and affordable way to navigate the city’s congested streets, particularly for short trips. However, their popularity has also led to a number of challenges, including an increase in accidents, complaints about sidewalk riding, and concerns about the safety of lithium-ion batteries.
The NYCDOT has reported a significant increase in e-bike and scooter-related accidents in recent years, prompting the city to step up enforcement efforts. In addition to confiscating illegally operated vehicles, the city has also issued fines for violations such as riding on sidewalks, running red lights, and failing to wear helmets. The city has also launched public awareness campaigns to educate riders about safe riding practices and the importance of complying with traffic laws.
Despite these efforts, many argue that the city’s approach to e-bike and scooter regulation remains fragmented and inconsistent. Some critics argue that the city’s regulations are too restrictive and fail to account for the needs of low-income workers who rely on e-bikes for their livelihoods. Others argue that the city needs to be more aggressive in enforcing existing regulations and cracking down on illegal operators.
The destruction of the confiscated e-bikes and scooters in Staten Island has become a flashpoint in the ongoing debate over e-bike and scooter regulation in New York City. While city officials defend the action as a necessary step to protect public safety, critics argue that it represents a wasteful and ineffective solution to a complex transportation challenge. The incident has highlighted the need for a more comprehensive and collaborative approach to regulating e-bikes and scooters, one that balances enforcement with education and infrastructure development.
The long-term impact of the Staten Island crackdown remains to be seen. It is possible that the destruction of the confiscated vehicles will deter some riders from operating illegally, but it is also possible that it will simply lead to a black market for unregistered e-bikes and scooters. Ultimately, the success of the city’s efforts to regulate e-bikes and scooters will depend on its ability to create a safe and sustainable environment for micromobility, one that addresses the concerns of all stakeholders.
The specific types of e-bikes and scooters crushed varied, but generally included models that had been illegally modified to exceed speed limits, those lacking proper safety features (such as lights and brakes), and those operated by individuals without required permits or licenses. Many of the confiscated vehicles were linked to commercial delivery services, where riders often face pressure to make quick deliveries, sometimes at the expense of safety and compliance.
The process leading up to the crushing involved multiple stages. First, law enforcement officers would identify and confiscate e-bikes and scooters that violated city regulations. These vehicles were then impounded and stored at a designated facility. Before destruction, attempts were made to identify the owners and provide them with an opportunity to reclaim their property, provided they could demonstrate compliance with all applicable regulations and pay any outstanding fines. However, in many cases, the vehicles were either unclaimed or deemed non-compliant, leading to their eventual destruction.
The environmental impact of crushing and disposing of these e-bikes and scooters is also a concern. The lithium-ion batteries used in these vehicles contain hazardous materials that can contaminate soil and water if not disposed of properly. City officials claim that the batteries were removed and recycled before the vehicles were crushed, but environmental advocacy groups have raised concerns about the potential for improper handling and disposal.
The debate over e-bike and scooter regulation in New York City is not unique. Many other cities around the world are grappling with similar challenges as they try to integrate these new forms of transportation into their existing infrastructure. Some cities have adopted more permissive approaches, allowing e-bikes and scooters to operate with minimal regulation, while others have implemented stricter rules and enforcement measures. The best approach likely depends on the specific characteristics of each city, including its population density, street layout, and transportation infrastructure.
Looking ahead, it is clear that e-bikes and scooters are here to stay. They offer a convenient and sustainable alternative to cars, particularly for short trips. However, their widespread adoption also requires a comprehensive and thoughtful regulatory framework that addresses safety concerns, promotes responsible riding behavior, and ensures equitable access for all users. The Staten Island crackdown serves as a reminder of the challenges involved in regulating micromobility and the need for a more collaborative and nuanced approach.
The political context surrounding the crackdown is also important to consider. City officials are under pressure to address the growing number of complaints about e-bike and scooter-related accidents and violations. The destruction of the confiscated vehicles may have been intended to send a message to riders that the city is serious about enforcing its regulations. However, the action has also been criticized as being politically motivated, with some suggesting that it was intended to appease voters who are concerned about the impact of e-bikes and scooters on their neighborhoods.
The economic impact of the crackdown is another important consideration. E-bikes and scooters are often used by low-income workers who rely on them for transportation and delivery services. The confiscation and destruction of these vehicles can have a significant impact on their livelihoods. Some advocacy groups have called for the city to provide financial assistance to low-income workers who have had their e-bikes and scooters confiscated, arguing that they should not be penalized for simply trying to make a living.
The social equity implications of the crackdown are also worth examining. E-bikes and scooters can provide access to transportation for people who may not be able to afford a car or who live in areas that are not well-served by public transportation. The confiscation and destruction of these vehicles could disproportionately affect low-income communities and people of color, who are more likely to rely on them for transportation.
The technological aspects of e-bike and scooter regulation are also evolving rapidly. New technologies, such as geofencing and speed limiting, could be used to automatically enforce regulations and prevent riders from operating in restricted areas or exceeding speed limits. However, there are also concerns about privacy and data security associated with these technologies.
The legal challenges surrounding e-bike and scooter regulation are also complex. Some riders have challenged the city’s regulations in court, arguing that they are overly restrictive or that they violate their constitutional rights. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, and it is likely that there will be further legal challenges to the city’s e-bike and scooter regulations in the future.
The ethical considerations surrounding e-bike and scooter regulation are also important to consider. Is it ethical for the city to confiscate and destroy e-bikes and scooters that are being used by low-income workers to make a living? Is it ethical for the city to impose regulations that disproportionately affect low-income communities and people of color? These are complex ethical questions that need to be addressed as the city develops its e-bike and scooter regulations.
The role of public education in promoting safe e-bike and scooter riding is also critical. The city needs to do more to educate riders about safe riding practices and the importance of complying with traffic laws. Public education campaigns should be targeted at all riders, regardless of their age, income, or ethnicity.
The importance of community engagement in developing e-bike and scooter regulations cannot be overstated. The city needs to engage with community members, advocacy groups, and other stakeholders to develop regulations that are fair, effective, and sustainable. Community engagement should be an ongoing process, not just a one-time event.
The need for data-driven decision-making in e-bike and scooter regulation is also essential. The city needs to collect data on e-bike and scooter usage, accidents, and violations in order to inform its regulatory policies. Data should be used to identify problem areas and to evaluate the effectiveness of different regulatory interventions.
The challenges of enforcing e-bike and scooter regulations are significant. The city needs to develop effective enforcement strategies that are both fair and efficient. Enforcement efforts should be focused on areas where there are high rates of accidents and violations.
The opportunities for innovation in e-bike and scooter regulation are also plentiful. The city should be open to experimenting with new regulatory approaches and technologies. Innovation can help to create a more safe, sustainable, and equitable environment for micromobility.
The importance of regional coordination in e-bike and scooter regulation is also important. E-bikes and scooters often cross municipal boundaries, so it is important for cities to coordinate their regulatory policies. Regional coordination can help to ensure that regulations are consistent and that riders are not confused by conflicting rules.
The role of the private sector in promoting safe e-bike and scooter riding is also important. E-bike and scooter companies should be responsible for ensuring that their riders are properly trained and that their vehicles are safe and well-maintained. The private sector can also play a role in funding public education campaigns and infrastructure improvements.
The need for long-term planning in e-bike and scooter regulation is also essential. The city needs to develop a long-term plan for micromobility that addresses the challenges and opportunities associated with e-bikes and scooters. The plan should be updated regularly to reflect changing conditions.
The success of e-bike and scooter regulation will depend on the ability of the city to address these challenges and opportunities in a comprehensive and collaborative manner. The Staten Island crackdown serves as a reminder of the complexities involved in regulating micromobility and the need for a more nuanced and sustainable approach. The incident has sparked a renewed debate about the best way to integrate e-bikes and scooters into the city’s transportation system.
The debate encompasses not only the immediate issues of safety and enforcement but also broader questions about urban planning, social equity, and environmental sustainability. Finding the right balance between promoting innovation and ensuring public safety will be crucial for the future of micromobility in New York City and other urban areas around the world.
The sheer number of vehicles crushed – hundreds in total – suggests a significant volume of violations, indicating a potentially widespread issue with non-compliance among e-bike and scooter users. This raises concerns about the effectiveness of existing regulations and enforcement strategies.
Furthermore, the visual impact of the crushing event, captured and disseminated widely through social media, has undoubtedly shaped public perception of e-bikes and scooters. While some may view it as a necessary deterrent, others may see it as an overreaction that unfairly targets a legitimate mode of transportation.
The event also raises questions about the economic value of the destroyed vehicles. While they may have been illegally operated, they still represent a significant investment, particularly for individuals who rely on them for their livelihood. The city’s decision to destroy them rather than explore alternative uses, such as donation to non-profit organizations or repurposing for parts, has been criticized as wasteful.
The long-term consequences of the Staten Island crackdown are uncertain. It remains to be seen whether it will lead to a sustained reduction in illegal e-bike and scooter operation or whether it will simply displace the problem to other areas of the city. The city’s ongoing efforts to develop a comprehensive and sustainable micromobility strategy will be critical to addressing these challenges in the long run.
The incident also highlights the need for greater collaboration between city agencies, community organizations, and the e-bike and scooter industry. By working together, these stakeholders can develop solutions that address the concerns of all parties and promote a safe, sustainable, and equitable transportation system.
The Staten Island e-bike and scooter crushing incident serves as a stark reminder of the challenges and opportunities associated with the rise of micromobility in urban areas. It underscores the need for a comprehensive and nuanced approach to regulation that balances enforcement with education, infrastructure development, and community engagement. Only by working together can we create a future where e-bikes and scooters can contribute to a more sustainable and accessible transportation system for all.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why did Staten Island crush hundreds of e-bikes and scooters?
The e-bikes and scooters were crushed as part of an enforcement action against illegally operated vehicles. According to city officials, the crushed vehicles were confiscated due to various violations, including illegal modifications, lack of proper registration, and operation in restricted areas. The city maintains that the crackdown is essential for public safety, citing concerns about reckless riding, sidewalk congestion, and the potential for battery fires.
2. What are the specific regulations that these e-bikes and scooters violated?
The specific regulations violated likely include:
- Illegal Modifications: Alterations to the vehicle that exceed speed limits or compromise safety features.
- Lack of Registration: Failure to register the e-bike or scooter with the city as required.
- Operation in Restricted Areas: Riding in areas where e-bikes and scooters are prohibited, such as sidewalks or certain parks.
- Failure to Comply with Safety Standards: Lack of proper safety equipment, such as lights, brakes, or helmets.
- Unlicensed Operation: Operating the vehicle without the required license or permit.
3. What are the criticisms of the city’s decision to crush the e-bikes and scooters?
Critics argue that the city’s resources could be better used to create safer infrastructure for e-bikes and scooters, as well as to educate riders and enforce existing regulations more effectively. They contend that simply crushing the vehicles does little to address the root causes of illegal operation and may disproportionately affect low-income workers who rely on e-bikes for transportation and delivery services. Some also view the action as wasteful, suggesting that the vehicles could have been donated or repurposed.
4. What is the city doing to promote safe e-bike and scooter riding?
The NYCDOT is actively working to implement a comprehensive e-bike and scooter program, which includes:
- Designated Bike Lanes: Creating dedicated lanes for cyclists and e-bike/scooter riders.
- Parking Regulations: Establishing designated parking areas for e-bikes and scooters to prevent sidewalk congestion.
- Safety Education Initiatives: Launching public awareness campaigns to educate riders about safe riding practices and traffic laws.
- Increased Enforcement: Stepping up enforcement efforts to crack down on illegal operation and violations.
5. What are the long-term solutions being considered for e-bike and scooter regulation in New York City?
Long-term solutions being considered include:
- Developing a Comprehensive Regulatory Framework: Creating clear and consistent regulations that address safety concerns, promote responsible riding behavior, and ensure equitable access for all users.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Expanding the network of bike lanes and designated parking areas to accommodate the growing number of e-bikes and scooters.
- Enhancing Public Education: Continuing to educate riders about safe riding practices and the importance of complying with traffic laws.
- Promoting Collaboration: Fostering collaboration between city agencies, community organizations, and the e-bike and scooter industry to develop effective solutions.
- Exploring New Technologies: Utilizing technologies such as geofencing and speed limiting to automatically enforce regulations and prevent riders from operating in restricted areas or exceeding speed limits.
- Addressing Equity Concerns: Providing financial assistance to low-income workers who rely on e-bikes for transportation and delivery services.